
Complete Guide to Password Security 2020
Password security is one of the most important parts of keeping your information safe online. Whether it’s your personal information, business information, or client information, having it compromised online can lead to a world of trouble, to say the least.
You may think your passwords are safe because only you know them, but that can often be proved wrong if your information is targeted. Check out the information below to see if your password security really makes the cut.
How Do Passwords Get Hacked?
As technology progresses, unfortunately so too do illegal uses for it. Hacking is no exception. While there are many different ways your password can be compromised, a few of the most common are described below:
- Phishing is a scheme hackers use to trick users into providing their passwords. This is often done through email but can also be done over the phone. In these scams hackers usually pose as a legitimate organization, such as the IRS, and demand information for those accounts.
- Brute force attacks use software that rapidly generates potential passwords and tries them. These types of software are incredibly fast and can find simple one-word passwords (such as “snowball”) and access the information protected by them within seconds.
- Credential stuffing is a type of attack in which hackers put information they’ve already stolen to use. Hackers will compile stolen logins, then use software that will run through the lists of stolen passwords and attempt to log in to other accounts using the same credentials.
The list above is by no means exhaustive. There are many ways hackers can and will attempt to access your logins. This is why it’s so important to use strong passwords to protect your information.
How to Create a Strong Password
To create a strong password, you should make sure your password checks several boxes:
- Use a long password, at least 16 characters
- Use both upper and lowercase letters in your password
- Use numbers in your password
- Use special characters in your password
- Use a random password, not one that’s easy to remember
Example:
Which is more secure: “OnceUpon@Time1993!” or “y@z?XLE!WN3KwcjT*5”?
| “OnceUpon@Time1993!” | “y@z?XLE!WN3NwcjT*5” |
| ✔ 18 characters | ✔ 18 characters |
| ✔ Upper & lowercase letters | ✔ Upper & lowercase letters |
| ✔ Numbers | ✔ Numbers |
| ✔ Special characters | ✔ Special characters |
| ✗ Random | ✔ Random |
Result: “y@z?XLE!WN3NwcjT*5” is more secure than “OnceUpon@Time1993!”
Why You Should Never Reuse Passwords
After creating a complicated, random password, it can be tempting to use it for several accounts, especially if you have it memorized. However, passwords should never be used for more than one account.
Remember the credential stuffing hacking method discussed earlier? It is a prime example of why having a unique password for every account is so important. If your accounts share passwords and one is hacked, the rest are instantly put at risk as well.
Why You Should Use a Password Manager
Remembering one long, complicated, random password may be a pain, but remembering dozens or more can be impossible. Luckily you can shred the piece of paper or sticky note you have them all written down on and replace it with a password manager.
A password manager is a program that will save all of your passwords. If you’re despairing over having to figure out yet another online program, don’t worry. Password managers are easy to use and there are plenty of free options available. A few benefits are mentioned below:
- Password Encryption – Password managers encrypt your login information, so it is never visible unless you choose to show it.
- Auto-Save – This setting can be personalized, but most password managers offer an option to automatically remember passwords. The next time you type in your password, simply choose to save it when your password manager prompts you to, usually with a small pop-up notification on your screen.
- Auto-Fill – Once your password is saved in a password manager, most have an auto-fill feature that can be used to quickly fill login fields without making your credentials visible. No more typing out long passwords, and your information stays encrypted throughout the entire process.
Not sure where to start finding a password manager? Some devices come with a built in password manager (if you’ve ever seen the option to save a password after typing it in, your device probably has one). Some others we recommend are listed below:
LastPass
Cost: Free or $3/month for Premium (other plans also available)
Includes:
- Secure encrypted password storage
- Password generator
- Multi-Factor Authentication
- Browser extension
- Mobile app
- Auto-save feature
- Auto-fill feature
- Digital wallet (to store payment information)
PassCamp
Cost: Free or ~$1.15/month for Premium (other plans also available)
Includes:
- Secure encrypted password storage (limit 25 with free plan)
- Password generator
- Multi-Factor Authentication
- Browser extension
- Mobile app (released 7/16/20)
- Auto-save feature
- Auto-fill feature
- History log (to keep a record of old passwords)
As you can see, both of these services have free plans available with everything you need to start protecting your passwords, including easy to use password storage, password encryption, Multi-Factor Authentication, browser extensions with auto-save and auto-fill features to make logging into your accounts quick and easy, and so on.
If you’re planning to use one of these services for your business, take a look at this comparison as there are some differences between them such as their sharing features, integration options, and support availability (be aware that PassCamp did roll out a mobile app on 7/16/20 and the linked comparison has not been updated to reflect this as of 7/21/20).
Why You Should Use Multi-Factor Authentication
Sometimes referred to as MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication), 2FA (Two Factor Authentication), or 2-step verification, this security feature allows you to require more than one login confirmation when signing into an account. It is available for many accounts today, including Facebook, Twitter, Google, and more. Below is an example of how to turn on MFA for a gmail account.
How to Turn on 2-step verification for Your GMail Account
On your laptop or desktop:
- Log in to your gmail account
- Click your user icon in the top right hand corner of the page
- Click “Manage Your Google Account”
- Click the “Security” option in the left-hand menu
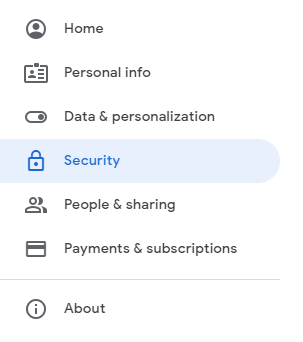
- Find the “Signing in to Google” section
- Click “2-Step Verification”
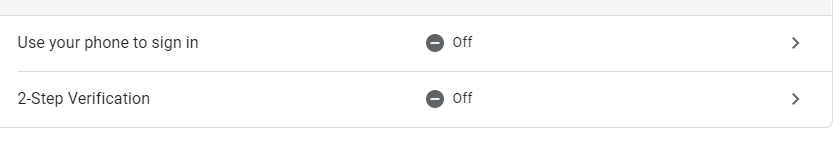
- Enter your password again
- Follow the set-up prompts as they are given
- Once you have completed the set-up, you will get a test prompt sent to your phone. It should look something like this:
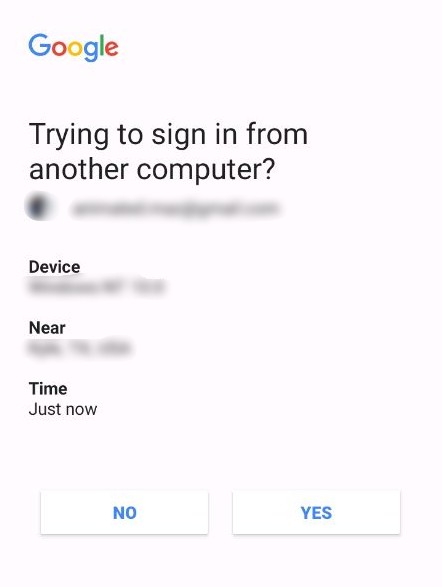
Once 2-step verification is successfully turned on you’ll receive a log in prompt on your phone whenever you sign in from a new device or location. If you ever receive a prompt when you are not attempting to access your account, you’ll know that your log in information has been compromised.
What to Do if a Password is Compromised
If you find out that a password has been compromised, or even if you suspect that it has been, you need to secure your account as soon as possible:
If you can still get into the account:
- Log in to the account
- Find your settings and change your password
- When prompted, choose to log out of all devices (make sure to remember your new password as this will log you out as well)
- Log back in to the account and review your security settings to make sure no settings were changed while the account was compromised.
If you cannot get into the account:
- This means that the hacker was able to change your password before you could
- If the account contained any saved payment information, contact your bank and have them take necessary security measures to protect your account
- Contact support for the account that was hacked and follow their recommendations to reclaim the account if possible.
Conclusion
Password security is an important part of keeping your information safe online. Create strong, unique passwords for all of your accounts, and protect them using a password manager and MFA. For additional information about keeping yourself safe online check out these articles:
Or contact tekRESCUE, a San Marcos IT services and digital marketing company, to learn how we can help.








