
Patch Perfect: Why Regular IT Updates Matter
What is IT patching? IT patching is the critical process of applying software updates to fix security vulnerabilities, bugs, and performance issues. These updates, or patches, are essential for maintaining the security and stability of your computer systems, operating systems, and applications.
Patches come in several forms, including:
- Security patches to fix vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit
- Bug fixes to resolve errors that cause crashes
- Feature updates to add new functionality
- Hotfixes for critical, time-sensitive emergencies
Think of it like car maintenance: you wouldn’t skip an oil change, and you shouldn’t run your business on unpatched software.
The stakes are high. The infamous WannaCry ransomware attack, for example, infected over 200,000 computers across 150 countries. This global crisis was preventable, caused by the failure to apply a readily available security patch.
Why does this matter for your business? Unpatched systems are a wide-open door for cyberattacks that can lead to data theft, operational shutdowns, and reputational ruin.
I’m Randy Bryan, founder of tekRESCUE and a cybersecurity expert. Throughout my experience with what is IT patching, I’ve seen how proper patch management is the difference between a secure business and a costly data breach.
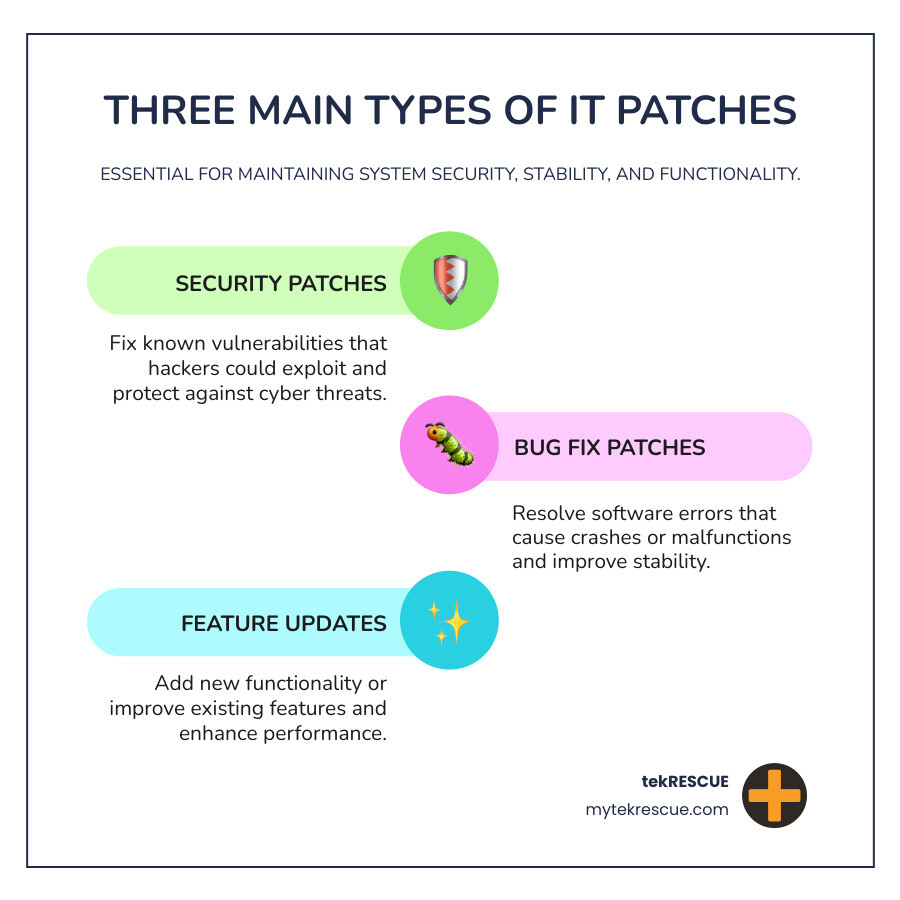
Table of Contents
What is IT Patching?
Software constantly evolves, and new security gaps emerge. This is where what is IT patching comes into play. It’s a fundamental practice in cybersecurity that ensures your digital tools remain robust, secure, and performant.
Defining the Terminology: Patch vs. Update, Bugfix, and Hotfix
While often used interchangeably, these terms have distinct meanings. Understanding them is key to effective patch management.
- A software patch is a targeted piece of code that modifies an existing program to fix a specific issue, like a security flaw or a bug, without changing the software’s version number.
- An update is a broader release that can include patches but often adds new features, improves performance, and typically changes the software’s version number.
- A bugfix is a type of patch specifically designed to correct a software error or “bug” that causes malfunctions or crashes.
- A hotfix is an emergency patch deployed rapidly to address a critical security vulnerability or a severe, system-destabilizing bug.
Here’s a table to help clarify the differences:
| Term | Definition | Purpose | Typical Deployment Speed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patch | A small, targeted modification to existing software. | Fixes specific issues (bugs, vulnerabilities) without changing core version. | Varies, often regular |
| Update | A broader release that can include patches, new features, and performance improvements. | Improves functionality, adds capabilities, and fixes bugs over a wider scope. | Scheduled (e.g., monthly) |
| Bugfix | A type of patch specifically designed to correct an error or defect in software. | Resolves specific software malfunctions, crashes, or incorrect behavior. | As needed, often in patches/updates |
| Hotfix | An urgent, emergency patch for critical vulnerabilities or severe bugs. | Provides immediate resolution to high-impact, time-sensitive problems. | Rapid, out-of-band |
The Patch Management Lifecycle: How Does IT Patching Work?
Effective patching is a structured, continuous process known as the patch management lifecycle. This ensures systems are updated securely without causing new problems.
The key stages include:
- Identification & Assessment: Continuously monitor vendor and security advisories for new patches. Use vulnerability scanning to pinpoint which systems need updates.
- Prioritization: Rank patches based on the severity of the vulnerability and the importance of the affected system. Critical security fixes take precedence.
- Testing: Before wide deployment, test patches in a controlled staging environment that mimics your live systems. This crucial step prevents a fix for one problem from causing another.
- Deployment: Roll out the tested patch to your systems. This is often automated and scheduled during off-peak hours to minimize business disruption.
- Verification & Monitoring: After deployment, verify that the patch was installed correctly and monitor systems for any new issues or performance changes.
- Documentation & Reporting: Maintain detailed records of all patching activities. This is vital for compliance, audits, and having a rollback plan if an issue arises.
The role of IT departments is to oversee this entire lifecycle, a continuous effort that keeps an organization’s IT infrastructure healthy and secure.
The Critical “Why”: Importance of Prompt and Regular Patching
Prompt and regular patching is a non-negotiable business imperative for several key reasons.
- Cybersecurity: Unpatched vulnerabilities are a primary entry point for attackers. The devastating WannaCry and Kaseya ransomware attacks both exploited known flaws for which patches were available.
- System Stability: Patches fix bugs that cause crashes, data corruption, and unexpected behavior, ensuring your software runs reliably and your team stays productive.
- Compliance: Regulations like HIPAA (healthcare) and PCI-DSS (payment cards) mandate that systems be kept secure and patched. Failure to comply can result in heavy fines and legal action.
The High Stakes of Neglect: Risks of Unpatched and EOL Software
Ignoring patch management is like playing Russian roulette with your business. The risks are substantial and can lead to devastating consequences.

When systems are left unpatched, they become prime targets for attackers, leading to:
- Data Breaches: Attackers exploit known weaknesses to steal sensitive customer, financial, and proprietary data.
- Financial Loss: The costs of a breach include downtime, remediation, legal fees, and regulatory fines, which can be crippling.
- Reputational Damage: A major security failure erodes customer trust and can permanently damage your brand’s standing in the market.
A particularly high-risk practice is using End-of-Life (EOL) software. When a vendor stops supporting a product, they no longer release security updates. Any new vulnerabilities found will never be patched, making EOL software a permanent and attractive target for cybercriminals.
The message is clear: proactive software updates are not optional. They are a critical shield against evolving threats and a cornerstone of business resilience. For more on this, read about The Importance of Software Updates.
Implementing a Rock-Solid Patch Management Strategy
Understanding what is IT patching is the first step; turning that knowledge into action is what protects your business. An effective patch management strategy is a systematic approach that secures your systems while ensuring smooth operations.
Best Practices: How to Approach IT Patching Strategically
An effective strategy is built on a foundation of clear policies and best practices.
- Maintain a Comprehensive Asset Inventory: You can’t protect what you don’t know you have. Catalog all software, hardware, and applications in your environment.
- Establish a Clear Policy: Define roles and responsibilities. Who identifies, tests, and approves patches? A clear framework prevents confusion during a crisis.
- Prioritize Based on Risk: Not all patches are equal. Use threat intelligence to prioritize critical security fixes for essential systems over minor updates for less important tools.
- Test in a Controlled Environment: Always test patches in a staging environment that mirrors your live systems. This helps catch compatibility or performance issues before they affect your business.
- Automate Where Possible: Use modern patch management tools to automate scanning, deployment, and reporting. Automation reduces human error and frees up your IT team for more strategic work.
- Integrate with Change Management: Schedule deployments during planned maintenance windows, communicate with users, and always have a rollback plan ready.
- Verify and Monitor Post-Deployment: After applying patches, confirm they were installed correctly and monitor systems for any unexpected behavior.
Organizations like the NIST Computer Security Resource Center provide excellent frameworks for developing these strategic approaches.
Automation and Outsourcing: Streamlining Your IT Patching Process
For many businesses, managing this process internally is overwhelming. This is where automation and outsourcing provide a strategic advantage.
Patch management software automates scanning, deployment, and reporting, reducing human error and saving time. However, these tools require expert management to be truly effective.
By partnering with a Managed Service Provider (MSP) like tekRESCUE, you gain access to specialized expertise and enterprise-grade tools without the overhead of hiring additional staff. We handle the entire patch management lifecycle for you, ensuring:
- Proactive Maintenance: We identify and address potential issues before they impact your operations, minimizing downtime.
- Expert Oversight: Our team stays current on emerging threats and best practices, applying that knowledge to protect your business.
- Compliance and Reporting: We provide the detailed documentation and audit trails required to meet regulatory standards like HIPAA or PCI-DSS.
Outsourcing patch management allows your team to focus on core business goals instead of routine IT maintenance. It’s about working smarter, not harder.
Don’t Let Your Business Fall Through the Cracks
Understanding what is IT patching is about recognizing its role as a cornerstone of modern business resilience. It’s not just a technical task but a fundamental strategy for protecting your assets, ensuring operational continuity, and maintaining customer trust. Neglecting patches or using End-of-Life software leaves your organization exposed to preventable threats like the WannaCry attack. A proactive strategy, whether managed in-house or through a partner, is essential.
The consequences of inaction are severe, leading to data breaches, financial loss, and operational disruptions that can cripple a business. Implementing a robust patch management strategy requires systematic inventory, risk-based prioritization, and thorough testing. For many organizations, the complexity and constant vigilance required make manual management impractical.
This is where strategic partnerships with experienced managed service providers can transform your security posture from reactive to proactive.
At tekRESCUE, we don’t just patch systems; we build resilient IT infrastructures that reduce risk and support growth. Our managed services combine comprehensive cybersecurity with strategies to boost your online presence, providing a holistic solution for businesses across Texas. We help you steer the complexities of IT security so you can focus on what you do best.
Don’t leave your business vulnerable to preventable cyber threats. The cost of proactive patch management pales in comparison to the potential devastation of a successful cyberattack. Take control of your IT security today.
Table of Contents









